WHAT VEGETABLES I CAN PLANT NOW?

Planting for the Seasons: How to Select Vegetables Based on the Climate Where You Live There is nothing like growing your own veggies for happiness. However, because different parts of the world have different climates, the season affects what you can successfully plant. With the help of this book, you will be able to plant vegetables with knowledge and awareness of the local climate and season.
Recognizing the Seasons for Planting:

Vegetable gardens usually flourish throughout two main seasons:
Vegetables of the “cool season” which occurs in the spring and fall, require mild frost and lower temperatures.
Warm Season: Warm season veggies are those that thrive in hot temperatures and are generally frost-sensitive. They dominate the summer months.
Planting based on Climate and Season:

Take into account the following while choosing the right veggies for your current planting window:
Where You Are Geographically: The USDA created planting zones to classify regions according to their average winter minimum temperatures. Identifying the veggies that are appropriate for your climate’s particular cold tolerance depends on knowing your planting zone.
Present Year: Whether you plant veggies from the cool or warm seasons depends on whether it’s spring, summer, or fall.
Planting Zone Considerations for Vegetables in the Spring (Cool Season):

In most places, spring is the best time to sow vegetables of the cool season. The breakdown by planting zone is as follows:
Zones 3-5: To prevent frost damage, early spring plantings in these colder zones can be made under row covers, or protective fabric tunnels. Carrots, beets, radishes, lettuce, spinach, and peas are good choices.
Zones 6–8: A greater variety of cool-season vegetables are available in these zones due to their warmer springs. Sow collard greens, Swiss chard, kale, lettuce, spinach, peas, carrots, beets, and radishes.
Zones 9–10: The window for some cool-season crops may be limited due to warmer springtime temperatures in these zones. Choose early spring plantings of lettuce, spinach, beets, and radishes.
Summertime Vegetable Planting (Warm Season) - Important Planting Zone Information

Vegetables that love the heat thrive in the summer. This is a planting zone-specific guide:
Zones 3-5: Move warm-season veggies begun indoors early once the risk of frost has passed. Melons, cucumbers, eggplant, squash, peppers, and tomatoes are all excellent options.
Zones 6–8: Warm season veggies have a longer summer window in these zones. Plant beans, maize, okra, cucumbers, melons, eggplant, squash, tomatoes, and peppers.
Zones 9–10: Extended harvests are possible in these zones because to the prolonged warm season. Savor an abundance of vegetables, including beans, sweet potatoes, melons, okra, eggplant, zucchini, and cucumbers.
Planting Zone Considerations for Fall Vegetables (Cool Season):

In many areas, fall provides a second opportunity to cultivate vegetables of the cool season. This is a breakdown of planting zones:
Zones 3-5: Plant seeds in late summer for fall harvest of cool season vegetables such as radishes, lettuce, spinach, and arugula. If there is a chance of frost, cover your plants with row covers.
Zones 6–8: For fall planting, take advantage of a broader assortment of chilly season veggies. Plant collard greens, lettuce, spinach, arugula, kale, and root crops like turnips, carrots, and beets.
Zones 9–10: Some cool-season vegetables can be harvested for longer thanks to the kinder fall weather. Plant some root vegetables, such as radishes and beets, along with lettuce and spinach.
Seasons for Planting Beyond Basics:
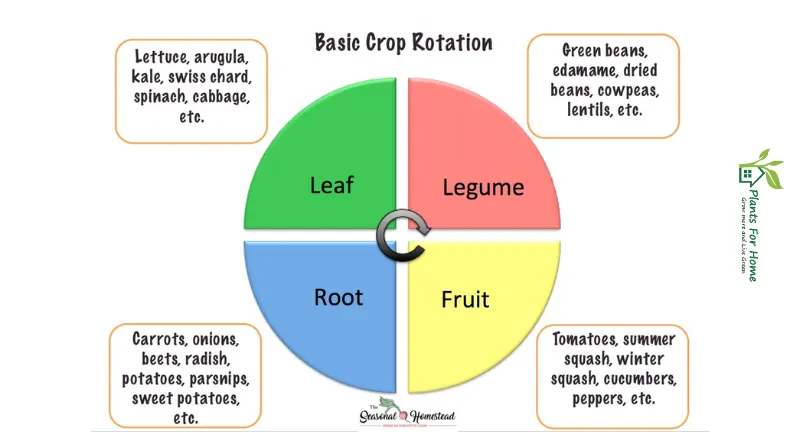
The major planting seasons are in the spring, summer, and fall, but some areas with mild winters may have longer planting seasons. Look into particular vegetables and whether they are suitable for your environment so that you can potentially plant all year round.
Extra Advice to Help You Plant Successfully:

Sunlight Requirements: Make sure your garden receives enough sunlight by learning about the requirements of each vegetable you decide to grow.
Soil Quality: For the best possible plant growth, the soil must be healthy and well-drained. If necessary, amend your soil to provide your chosen crops the proper nutrients and drainage. Seed beginning: You can prolong your harvest season by beginning some warm-season vegetable seeds indoors before moving them outside.
Water Often: Keep your garden consistently moist, especially in the summer when it’s hot and dry.
Mulch: Covering your plants with mulch will assist the soil retain moisture, keep weeds at bay, and maintain a consistent temperature.
CONCLUSION:
You may plant veggies with confidence and have a year-round, profitable garden by knowing the planting seasons, taking your climate and planting zone into account, and heeding these helpful suggestions. Recall to do your homework on particular vegetable varieties and whether they are suitable for growing in your area.











